This is an introduction to the Apache Spark Tutorial. In this Spark tutorial, you will learn about the Spark architecture and how to install and setup Spark in Window and Mac. You will learn how to write and execute Spark codes in Scala and Python.
1. Overview of Apache Spark
Apache Spark is an open source cluster computing technology developed to perform analytical data processing on large scale distributed data. It is a processing engine developed at University of California and open-sourced to Apache Software Foundation.
Spark is build as an extension of Hadoop MapReduce and optimized to run in memory. This means it provides extremely fast performance compared to similar technologies. Therefore Spark is considered a Top-Level Apache project.
Spark is used for a variety of data analysis operations including data integration, machine learning stream processing and interactive analytics.
2. The Spark Architecture
The Spark architecture consists of a driver program, cluster manager and worker nodes. Spark uses the master-slave architecture where the driver program is the master and the worker nodes are the slaves.
When an Apache Spark application is started, the driver program creates a context. The context is an entry point to your Spark application. Then all the operations and processing are performed on the worker nodes. The resources are managed by the Cluster Manager.
The Spark Architecture is shown below:

The components of the Spark architecture is explained below
- Driver Program – This is the program that runs the main() function of a Spark application. It creates the SparkContext. The SparkContext cordinates the Spark application.
- Cluster Manager – Manages the cluster and allocates resources across a Spark application.
- Worker Node – This is the slave node that runs the application on the cluster
- Executor – It is a process created to run application on a worker node. It runs tasks and provides memory and storages across the tasks.
- Task -This is a unit of work that is run by on executor process.
3. Components of Spark
To understand and work with Spark, you need to understand its components. These components are tightly integrated.
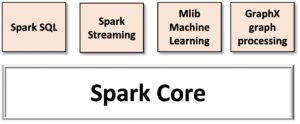
The Components of Spark are explained below:
Spark Core
Spark Cor is the main base library of Spark. It performs the core functionalities including
- task scheduling
- memory management
- fault recovery
- I/O functionalities etc
Spark SQL
This is build on top of the Spark Core and provides support for structured data. It allows for querying data using SQL as well as other SQL variants such as HQL (Hive Query Language)
Spark Streaming
This is a module that provides functionality for performing Stream analytics, that is processing on streaming data. Streaming is enabled by Spark Core’s scheduling capability. Data is ingested in mini-batches and RDD transformations are performed
MLLib
This is the Machine Learning library of Spark. It contains various machine learning algorithms. Some of the algorithms includes those for
- Classification
- Regression
- Clustering
- Principal Components Analysis
- Hypothesis Testing
GraphX
This is the Spark library used for manipulating graphs. It is also used for parallel computing. Directed graphs can be created and processed using this module. Some operations on graphs include:
- aggregate messages
- joining vertices
- creating sub-graphs
4. Features of Apache Spark
These features of Spark can also be regarded as the benefits of Spark
- In-Memory processing
- Fault-tolerance
- Supports variety of clusters managers including Spark, Mesos, Yarn etc
- Multiple language support – this means that Spark provides built-in APIs in Java, Scala and Python. So Spark applications can be written in these languages
- In-built optimization when using DataFrames
- Lightweight and easy to use
- Can run on the cloud and standalone